Key Networking Devices: Routers, Switches, and Modems
Okay, here’s a thorough outline and a detailed long-form article about key networking devices, written in the style you requested. I’ve incorporated all your specific requirements.
Outline
Here is a detailed outline presented in a table format:
| Section | Heading | Description | LSI Keywords |
| :———– | :————————————————————————— | :—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— | :———————————————————————————————————- |
| 1 | Genesis of Network Connectivity | Briefly touch upon the history of networking, setting the stage for the introduction of modern networking devices. | Internet history, network evolution, telecommunications, early internet |
| 1.1 | From ARPANET to the Internet | Discuss the transition from basic networks to the complex interconnected systems we use today. | ARPANET, packet switching, TCP/IP, World Wide Web |
| 2 | Demystifying Network Hardware | Introduce the core components that make up the backbone of network infrastructure. | Network devices, hardware components, data transmission, network infrastructure |
| 2.1 | The Role of Hardware in Digital Communication | Explain how these devices facilitate the flow of facts across networks. | Digital communication, data packets, signal processing, network connectivity |
| 3 | In Depth with Internet Gateways | Focus on routers, highlighting their function as the primary managers of network traffic. | Gateway devices, internet routers, path determination, traffic routing |
| 3.1 | Defining the Router’s Domain | Clear up misconceptions about what routers do and do not do. | Router functions, IP addresses, network segmentation, routing protocols |
| 3.2 | Routing Mechanisms Unveiled | Delve into the technical aspects of how routers direct traffic,including routing tables and protocols. | Routing tables, dynamic routing, static routing, network protocols, BGP, OSPF |
| 3.3 | The Router’s Role in Network Security | Explore how routers are involved in securing networks from external threats. | network security, firewalls, NAT, access control lists, VPN |
| 3.4 | Routers and the Home Network | Discuss the practical use of routers in residential settings. | Home networking, Wi-Fi setup, internet sharing, device connectivity |
| 4 | The Intricacies of Network bridges | An exploration of switches and their critical role in local area networks (LANs). | Network bridges, LAN devices, network connectivity, packet switching, bridges |
| 4.1 | Understanding Switch functionality | Explain what switches are and how they differ from routers. | Switch vs. router, data linking, MAC addresses, Ethernet |
| 4.2 | Types of Switches: Managed vs. Unmanaged | Differentiate between the various kinds of switches and their capabilities. | Managed switches, unmanaged switches, VLANs, QoS, network management |
| 4.3 | Switches in Enterprise Networks | Discuss the use of switches in larger, more complex network environments. | Enterprise networks, network scalability, redundancy, network topology |
| 4.4 | Optimizing Network Performance with Switches | Explore how switches can enhance the efficiency and speed of a network. | Network optimization, bandwidth management, traffic prioritization, network speed |
| 5 | Decoding the Language of the Internet | A focused look at modems and their role as translators between digital data and communication signals. | Internet language, data translation, modulation, demodulation |
| 5.1 | Modem: The Internet’s Translator | Clarify the function of modems in converting signals for internet connectivity. | Signal conversion, analog signals, digital signals, data transmission |
| 5.2 | Types of Modems: Cable, DSL, Fiber | Break down the different types of modems based on their connection technology. | Cable modem, DSL modem, fiber optic modem, satellite modem, dial-up |
| 5.3 | Evolution of Modem Technology | Trace the progress of modems from their early, slower forms to today’s high-speed devices. | Modem history, baud rate, broadband, data transfer rates |
| 5.4 | Modems in the Age of High-speed Internet | Discuss the relevance of modems in modern high-bandwidth internet environments. | high-speed internet, gigabit internet, bandwidth capacity, internet service providers (ISPs) |
| 6 | Synergy in Network Devices | Examine how routers, switches, and modems work together to create a functional network. | Network synergy,device interaction,integrated networks,network architecture,device collaboration |
| 6.1 | Creating a Cohesive Network Surroundings | Illustrate the typical setup where these devices interact. | Network setup, device configuration, internet connection, home network diagram |
| 6.2 | Troubleshooting Common Network Issues | Provide basic tips for resolving common problems related to these devices. | Network troubleshooting, connectivity issues, slow internet, Wi-Fi problems |
| 7 | The Forefront of Network Innovation | Discuss the latest trends and advancements in networking technology.| Network innovation, emerging technologies, future of networking, advanced networking |
| 7.1 | emerging Technologies in Networking | Explore new developments like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). | SDN, NFV, cloud networking, IoT, 5G |
| 7.2 | The Future of Routers, Switches, and Modems | Speculate on the future evolution of these devices in response to technological advancements. | Future of routers, smart homes, intelligent networks, network automation |
| 8 | Looking Ahead: The Next Generation of Network infrastructure | conclude by reflecting on the ongoing evolution of networking and its impact on our digital lives. | Future of the internet, network evolution, digital conversion, connectivity advancements |
| 8.1 | The Continued Importance of Networking Devices | Reiterate the essential role these devices will continue to play in an increasingly connected world. | Importance of networking, global connectivity, internet accessibility, digital future |
Article: Key Networking Devices
In a world where staying connected is as essential as, well, breathing, understanding the mechanisms behind our digital lifelines is paramount. Imagine trying to navigate a bustling city without roads or traffic lights; similarly, our interconnected globe relies on specific hardware to ensure the smooth flow of data.
Key Networking Devices in Portuguese
%%Português%%: Principais dispositivos de rede: roteadores, switches e modems
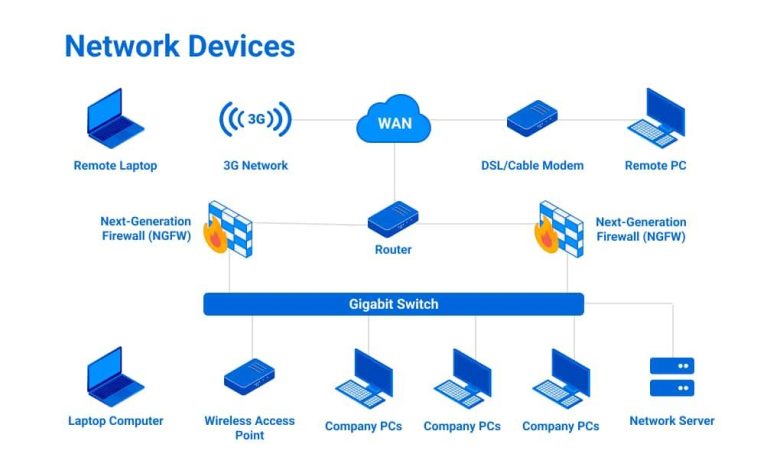
Os roteadores, switches e modems são os principais dispositivos de rede que permitem que os dispositivos se conectem à internet e uns aos outros. Embora possam parecer semelhantes, cada um tem uma função diferente na rede.
Roteadores:
Os roteadores são os mais complexos dos três e são responsáveis por conectar várias redes juntas.Encaminham pacotes de dados entre redes e podem ser usados para conectar uma rede doméstica ou de escritório à internet. Os roteadores também podem ser usados para criar redes privadas virtuais (VPNs), que permitem acessar com segurança os recursos da rede a partir de um local remoto. O roteador atribui um endereço IP local a cada dispositivo na rede local para que possa identificar cada dispositivo e garantir que os dados sejam enviados para o destino correto.
Switches:
Os switches são usados para conectar vários dispositivos na mesma rede. Encaminham pacotes de dados entre dispositivos na rede e podem ser usados para criar redes locais (LANs). Os switches mantêm uma tabela de endereços MAC da rede local, que usa para determinar o destino de cada pacote de dados.
Os switches operam na camada de enlace de dados (Camada 2) do modelo OSI e usam endereços MAC para encaminhar tráfego para o destino correto. Os switches podem ser gerenciados ou não. Os switches não gerenciados são dispositivos plug-and-play que não exigem nenhuma configuração. Os switches gerenciados são mais complexos e oferecem recursos como VLANs, QoS e espelhamento de portas.
Modems:
Os modems são usados para conectar uma rede à internet. Modulam e demodulam sinais, permitindo que os dados sejam transmitidos através de linhas telefônicas, linhas de cabo ou conexões sem fio. Os modems são essenciais para conectar uma rede doméstica ou